

VMware virtualizes physical computers using its core hypervisor product. These are the various components of VMware virtualization and how they work. A network of 75,000 partners supports customers with a wide variety of add-on products and services.
Industry support: VMware is the foremost provider of virtualization services, with over 500,000 customers.Fewer physical servers require less space in your data center and less energy to power and cool. More efficient use of energy and space: VMware lets you run more applications using fewer physical servers.With VMware, you can run each application in its own OS on the same physical server and make better use of the physical server’s available CPU power. One way to eliminate this risk is to run each application in its own OS on its own dedicated physical server, but this is inefficient because each OS might only use 30% of a server's CPU power. Administrators don't like running multiple mission-critical applications on a single server OS because if one application crashes, it can make the OS unstable and crash other applications. Improved return on investment (ROI): VMware enables you to use more of a physical computer's resources.Using VMware products and services for virtualization brings several benefits.
#Vmware vs virtualbox software
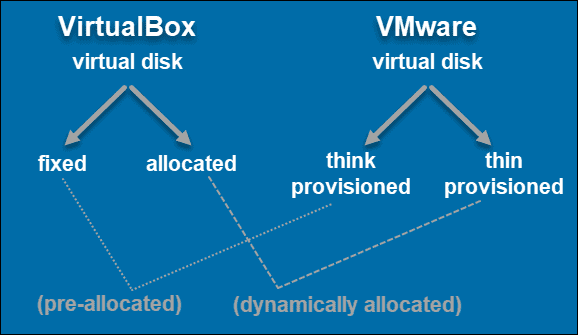
For example, you could enable your software development environment to create a virtual machine that it could use to test a software program.įor more information on virtual machines, see " Virtual Machines: A Complete Guide." You can also use the vSphere Web Services software development kit to configure VMs via other programs. You can configure virtual machine settings using the vSphere Client, which is a command-line interface for VM management. VMware offers various tools for managing these files. An operating system (OS) running in a VM is called a guest OS.Įach VM includes a configuration file that stores the VM’s settings, a virtual disk file that is a software version of a hard drive, and a log file that keeps track of the VM’s activities, including system failures, hardware changes, migrations of virtual machines from one host to another, and the VM’s status. A VM is a software-based representation of a physical computer. VMware’s virtualization products are now a crucial part of many enterprises' IT infrastructures.įor a visual presentation of the concept of virtualization, see our video “Virtualization Explained”: See "Virtualization: A Complete Guide" for a comprehensive overview.Ī virtual machine (VM) is the base unit of VMware virtualization. It also enables cloud providers- public or private- to serve more users with their existing physical computer hardware. Each virtual machine runs its own operating system (OS) and behaves like an independent computer, even though it is running on a portion of the actual underlying computer hardware.Īs you can imagine, virtualization enables more efficient utilization of computer hardware and enables a greater return on an organization’s hardware investment. Virtualization software creates an abstraction layer over computer hardware that allows the hardware elements of a single computer- processors, memory, storage, and more- to be divided into multiple virtual computers, commonly called virtual machines (VMs). Simply put, VMware (link resides outside ibm.com) develops virtualization software.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
